java tutorial - Java datatypes and literals | Primitive and reference data types, literals - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
- Variables are nothing more than reserved memory locations for storing values. This implies when you create variable, you reserve a few space in memory.
- Based on the type of data which is assigned to the variable, the OS allocates memory and chose what should be stored in the reserved memory.
- Hence, by assigning several data types to variables, the programming language Java will store integers, decimals and characters in these variables.
There are two types of data in Java:
- Simple or primitive data types;
- Referential data types (reference / object).
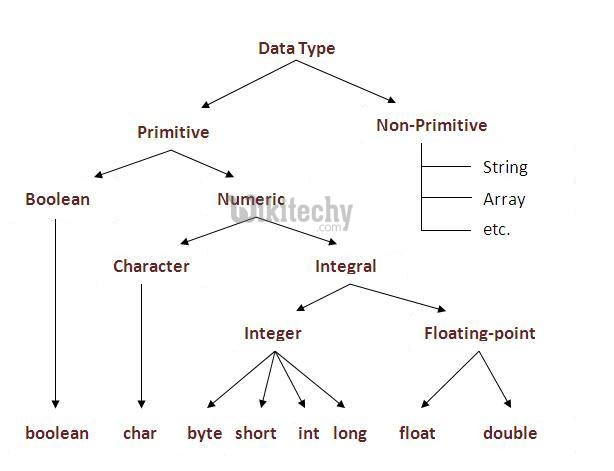
Primitive data types
- There are 8 types of data are supported by Java. The most important data types are predefined by the language and are named for the keyword.
- Now let's look in detail at these eight basic data types existing in the Java programming language.


Byte type in java
- The byte data type is an 8-bit signed integer.
- The minimum value is -128 (-2 7).
- The maximum value is 127 (inclusive) (2 7 -1).
- The default is 0.
- byte is designed to save space in large arrays, mostly instead of integers, because byte is four times smaller than int.
Example:
byte a = 100;
byte b = -50;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Short type in Java
- The short data type is a 16-bit signed integer.
- The minimum value is -32768 (-2 15).
- The maximum value is 32,767 (inclusive) (2 15 -1).
- The short type in Java can also be used to save memory as byte. The size of short is 2 times less than int.
- The default is 0.
- Example:
short s = 10000;
short r = -20000;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Int type in java
- In Java, the int data type is a 32-bit signed integer.
- The minimum size int is 2 147 483 648 (-2 31).
- The maximum value is 2,147,483,647 (inclusive) (2 31 -1).
- The int type is usually used for integer values. If there is no concern about memory.
- The default is 0.
- Example:
int a = 100000;
int b =-200000;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
long type in Java
- The long data type is a 64-bit signed integer.
- The minimum value is - 9,223,372,036,854,775,808 (-2 63 ).
- The maximum value is 9,223,372,036,854,775.807 (inclusive). (2 63 -1).
- In Java Applies when a wider range than int is required.
- The default is 0L.
- Example:
long a = 100000L;
long b =-200000L;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Float type in java
- The data type float is a single precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.
- The float type is mainly used to store memory in large arrays of floating-point numbers.
- The default is 0.0f.
- The float type should never be used for an exact value, such as currency.
- Example:
float f1 = 234.5f;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
double datatype in java
- The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point.
- Usually used for decimal values.
- The double type should never be used for an exact value, such as a currency.
- The default is 0.0d.
- Example:
double d1 = 123.4;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Boolean datatype in java
- The boolean data type is one bit of information.
- There are only two possible values: true and false.
- It is intended for simple signs that allow you to track conditions true or false.
- The default is false.
- Example:
boolean one = true;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
char datatype in java
- The char data type is one 16-bit Unicode character.
- The minimum value is "\ u0000" (or 0).
- The maximum value is "\ uffff" (or 65535 inclusive).
- In Java, a char is needed to store any character.
- Example:
char letterA ='A';click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Reference data types
- Reference variables are created using certain class constructors. They are designed to access objects. These variables are declared with a specific type that can not be changed. For example, Employee, Puppy, etc.
- Class objects and different kinds of array variables fall under the reference data type .
- In Java, by default, the value of several reference variable is invalid (null).
- A reference variable can be used to refer several object declared or of any compatible type.
- Example:
Animal animal = new Animal("giraffe");click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Literals in Java
Literals in Java represent the representation of the source code as a fixed value. A Literals is represented directly in the code with no computation. A literal in Java can be assigned to several variables from the core type. For example:
- Byte, int, long, and short can be expressed in decimal (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16), or octal (base 8) by the calculus.
- When using literals in Java, the 0 prefix is used to specify the octal system, and the 0x prefix indicates a hexadecimal system. For example:
int decimal = 100;
int octal = 0144;
int hexa = 0x64;click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
- String literals in the Java language are defined as in most other languages, enclosing a sequence of characters between a pair of double quotes. Examples of string literals:
"Hello World"
"two\nlines"
"\"This is in quotes\""click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Types of literals String and char can contain any Unicode characters. For example:
char a = '\u0001';
String a = "\u0001";click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
The Java language supports several special escape sequences for the String and char literals:
| Notation | Performance |
| \ n | New line (0x0a) |
| \ r | Carriage return (0x0d) |
| \ f | Page run (0x0c) |
| \ b | Return to step (0x08) |
| \ s | space (0x20) |
| \ t | Tabulation |
| \ " | Double quote |
| \ ' | Apostrophe |
| \\ | Backslash |
| \ ddd | Octal symbol (ddd) |
| \ uxxxx | Hexadecimal character UNICODE (xxxx) |
